撰写双端平台代码(插件编写实现)
学习如何撰写原生实现的代码。
本指南将介绍如何在 Flutter 中使用特定于平台的原生自定义代码。
概览
#你可以在 Flutter 应用中使用特定于平台的代码。常见的几种方法包括:
-
使用 Flutter 的平台通道 API 在 Flutter 和所需平台之间传递信息。更多信息,请参阅 使用平台通道调用特定平台的代码。
-
使用
Pigeonpackage 生成类型安全的特定平台代码。更多信息,请参阅 使用 Pigeon package 调用特定平台的代码。
Flutter 支持以下平台和平台特定语言:
- Android: Kotlin, Java
- iOS: Swift, Objective-C
- Windows: C++
- macOS: Objective-C
- Linux: C
平台通道架构概述
#消息使用平台通道在客户端(UI)和宿主(平台)之间传递,如下图所示:
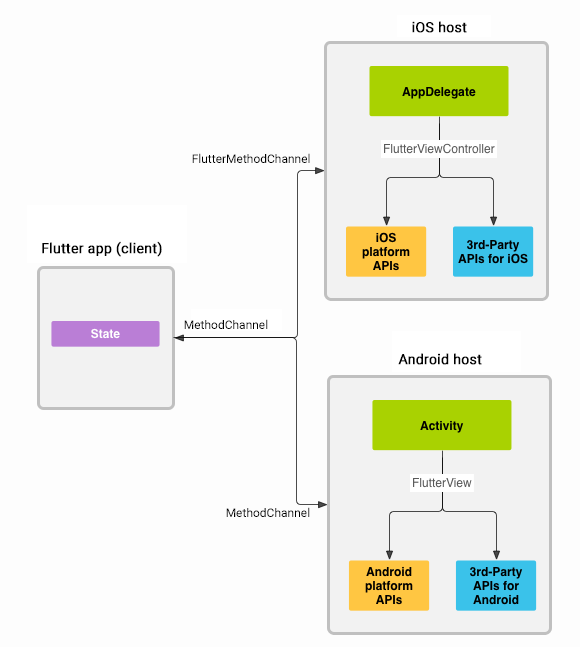
在上图中,消息和响应以异步的形式进行传递,以确保用户界面能够保持响应。在客户端,Flutter 的 MethodChannel
可以发送与方法调用相对应的消息。在对应平台,Android 的 MethodChannel
和
iOS 的 FlutterMethodChannel
可以接收方法调用并发回结果。通过这些类,你只需很少的 模板 代码就能开发平台插件。
数据类型支持
#
标准平台通道 API 和 Pigeon pacakge
使用名为 StandardMessageCodec
的标准消息编解码器,该编解码器支持简单的类似 JSON 的值,且为高效二进制序列化,例如布尔值、数字、字符串、字节缓冲区及这些类型的列表和映射。在发送和接收值时,它会自动将这些值进行序列化和反序列化。
下表展示了如何在平台端接收 Dart 值,反之亦然:
| Dart | Kotlin |
|---|---|
null | null |
bool | Boolean |
int (<=32 bits) | Int |
int (>32 bits) | Long |
double | Double |
String | String |
Uint8List | ByteArray |
Int32List | IntArray |
Int64List | LongArray |
Float32List | FloatArray |
Float64List | DoubleArray |
List | List |
Map | HashMap |
| Dart | Java |
|---|---|
null | null |
bool | java.lang.Boolean |
int (<=32 bits) | java.lang.Integer |
int (>32 bits) | java.lang.Long |
double | java.lang.Double |
String | java.lang.String |
Uint8List | byte[] |
Int32List | int[] |
Int64List | long[] |
Float32List | float[] |
Float64List | double[] |
List | java.util.ArrayList |
Map | java.util.HashMap |
| Dart | Swift |
|---|---|
null | nil (NSNull when nested) |
bool | NSNumber(value: Bool) |
int (<=32 bits) | NSNumber(value: Int32) |
int (>32 bits) | NSNumber(value: Int) |
double | NSNumber(value: Double) |
String | String |
Uint8List | FlutterStandardTypedData(bytes: Data) |
Int32List | FlutterStandardTypedData(int32: Data) |
Int64List | FlutterStandardTypedData(int64: Data) |
Float32List | FlutterStandardTypedData(float32: Data) |
Float64List | FlutterStandardTypedData(float64: Data) |
List | Array |
Map | Dictionary |
| Dart | Objective-C |
|---|---|
null | nil (NSNull when nested) |
bool | NSNumber numberWithBool: |
int (<=32 bits) | NSNumber numberWithInt: |
int (>32 bits) | NSNumber numberWithLong: |
double | NSNumber numberWithDouble: |
String | NSString |
Uint8List | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithBytes: |
Int32List | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithInt32: |
Int64List | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithInt64: |
Float32List |
FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithFloat32: |
Float64List |
FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithFloat64: |
List | NSArray |
Map | NSDictionary |
| Dart | C++ |
|---|---|
null | EncodableValue() |
bool | EncodableValue(bool) |
int (<=32 bits) | EncodableValue(int32_t) |
int (>32 bits) | EncodableValue(int64_t) |
double | EncodableValue(double) |
String | EncodableValue(std::string) |
Uint8List | EncodableValue(std::vector<uint8_t>) |
Int32List | EncodableValue(std::vector<int32_t>) |
Int64List | EncodableValue(std::vector<int64_t>) |
Float32List | EncodableValue(std::vector<float>) |
Float64List | EncodableValue(std::vector<double>) |
List | EncodableValue(std::vector<EncodableValue>) |
Map |
EncodableValue(std::map<EncodableValue, EncodableValue>) |
| Dart | C (GObject) |
|---|---|
null | FlValue() |
bool | FlValue(bool) |
int | FlValue(int64_t) |
double | FlValue(double) |
String | FlValue(gchar*) |
Uint8List | FlValue(uint8_t*) |
Int32List | FlValue(int32_t*) |
Int64List | FlValue(int64_t*) |
Float32List | FlValue(float*) |
Float64List | FlValue(double*) |
List | FlValue(FlValue) |
Map | FlValue(FlValue, FlValue) |
示例: 通过平台通道调用特定平台的代码
#
以下代码演示了如何调用平台相关 API 来检索并显示当前的电池电量。它通过平台消息 getBatteryLevel()
来调用 Android 的 BatteryManager API、
iOS 的 device.batteryLevel API、以及 indows 上的 GetSystemPowerStatus。
该示例在主应用程序中添加平台相关代码。如果想要将该代码重用于多个应用程序,那么项目的创建步骤将略有差异(查看 Flutter Packages 的开发和提交),但平台通道代码仍以相同方式编写。
第一步:创建一个新的应用项目
#首先创建一个新的应用:
-
在终端中运行:
flutter create batterylevel
默认情况下,我们的模板使用 Kotlin 编写 Android 或使用 Swift 编写 iOS 代码。要使用
Java 或 Objective-C,请使用 -i 和/或 -a 标志:
-
在终端中运行:
flutter create -i objc -a java batterylevel
第二步:创建 Flutter 平台客户端
#应用程序的 State 类保持当前应用的状态。扩展它以保持当前的电池状态。
首先,构建通道。在返回电池电量的单一平台方法中使用 MethodChannel。
通道的客户端和宿主端通过传递给通道构造函数的通道名称进行连接。一个应用中所使用的所有通道名称必须是唯一的;使用唯一的 域前缀 为通道名称添加前缀,比如:samples.flutter.dev/battery。
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
static const platform = MethodChannel('samples.flutter.dev/battery');
// Get battery level.
接下来,在方法通道上调用方法(指定通过 String 标识符 getBatteryLevel
调用的具体方法)。调用可能会失败—比如,如果平台不支持此平台
API(比如在模拟器中运行),所以将 invokeMethod 调用包裹在 try-catch 语句中。
在 setState 中使用返回结果来更新 _batteryLevel 内的用户界面状态。
// Get battery level.
String _batteryLevel = 'Unknown battery level.';
Future<void> _getBatteryLevel() async {
String batteryLevel;
try {
final result = await platform.invokeMethod<int>('getBatteryLevel');
batteryLevel = 'Battery level at $result % .';
} on PlatformException catch (e) {
batteryLevel = "Failed to get battery level: '${e.message}'.";
}
setState(() {
_batteryLevel = batteryLevel;
});
}
最后,将模板中的 build 方法替换为包含以字符串形式显示电池状态、并包含一个用于刷新该值的按钮的小型用户界面。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Material(
child: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _getBatteryLevel,
child: const Text('Get Battery Level'),
),
Text(_batteryLevel),
],
),
),
);
}
步骤 3: 添加 Android 平台的实现
#首先在 Android Studio 中打开 Flutter 应用的 Android 宿主部分:
启动 Android Studio
-
选择菜单项 File > Open...
-
导航到包含 Flutter 应用的目录,然后选择其中的 android 文件夹。点击 OK。
-
在项目视图中打开 kotlin 文件夹下的
MainActivity.kt文件。
在 configureFlutterEngine() 方法中创建一个 MethodChannel 并调用
setMethodCallHandler()。确保使用的通道名称与 Flutter 客户端使用的一致。
import androidx.annotation.NonNull
import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterActivity
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngine
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel
class MainActivity: FlutterActivity() {
private val CHANNEL = "samples.flutter.dev/battery"
override fun configureFlutterEngine(@NonNull flutterEngine: FlutterEngine) {
super.configureFlutterEngine(flutterEngine)
MethodChannel(flutterEngine.dartExecutor.binaryMessenger, CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler {
call, result ->
// This method is invoked on the main thread.
// TODO
}
}
}
添加使用 Android battery API 来检索电池电量的 Android Kotlin 代码。该代码与你在原生 Android 应用中编写的代码完全相同。
首先在文件头部添加所需的依赖:
import android.content.Context
import android.content.ContextWrapper
import android.content.Intent
import android.content.IntentFilter
import android.os.BatteryManager
import android.os.Build.VERSION
import android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES
然后在 MainActivity 类中的 configureFlutterEngine() 方法下方添加以下新方法:
private fun getBatteryLevel(): Int {
val batteryLevel: Int
if (VERSION.SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
val batteryManager = getSystemService(Context.BATTERY_SERVICE) as BatteryManager
batteryLevel = batteryManager.getIntProperty(BatteryManager.BATTERY_PROPERTY_CAPACITY)
} else {
val intent = ContextWrapper(applicationContext).registerReceiver(null, IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED))
batteryLevel = intent!!.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_LEVEL, -1) * 100 / intent.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SCALE, -1)
}
return batteryLevel
}
最后,完成前面添加的 onMethodCall() 方法。你需要处理单个平台方法 getBatteryLevel(),所以在参数 call 中对其进行验证。该平台方法的实现是调用上一步编写的 Android 代码,并使用 result 参数来返回成功和错误情况下的响应。如果调用了未知方法,则报告该方法。
删除以下代码:
MethodChannel(flutterEngine.dartExecutor.binaryMessenger, CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler {
call, result ->
// This method is invoked on the main thread.
// TODO
}
并替换成以下内容:
MethodChannel(flutterEngine.dartExecutor.binaryMessenger, CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler {
// This method is invoked on the main thread.
call, result ->
if (call.method == "getBatteryLevel") {
val batteryLevel = getBatteryLevel()
if (batteryLevel != -1) {
result.success(batteryLevel)
} else {
result.error("UNAVAILABLE", "Battery level not available.", null)
}
} else {
result.notImplemented()
}
}
首先在 Android Studio 中打开 Flutter 应用的 Android 宿主部分:
启动 Android Studio
-
选择菜单项 File > Open...
-
导航到包含 Flutter 应用的目录,然后选择其中的 android 文件夹。点击 OK。
-
在项目视图中打开 java 文件夹下的
MainActivity.java文件。
接下来,在 configureFlutterEngine() 方法中创建一个 MethodChannel 并设置一个
MethodCallHandler。确保使用的通道名称与 Flutter 客户端使用的一致。
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterActivity;
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngine;
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel;
public class MainActivity extends FlutterActivity {
private static final String CHANNEL = "samples.flutter.dev/battery";
@Override
public void configureFlutterEngine(@NonNull FlutterEngine flutterEngine) {
super.configureFlutterEngine(flutterEngine);
new MethodChannel(flutterEngine.getDartExecutor().getBinaryMessenger(), CHANNEL)
.setMethodCallHandler(
(call, result) -> {
// This method is invoked on the main thread.
// TODO
}
);
}
}
添加使用 Android battery API 来检索电池电量的 Android Java 代码。该代码与你在原生 Android 应用中编写的代码完全相同。
首先在文件头部添加所需的依赖:
import android.content.ContextWrapper;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.os.BatteryManager;
import android.os.Build.VERSION;
import android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES;
import android.os.Bundle;
然后在 Activity 类中的 onCreate() 方法下方添加以下新方法:
private int getBatteryLevel() {
int batteryLevel = -1;
if (VERSION.SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
BatteryManager batteryManager = (BatteryManager) getSystemService(BATTERY_SERVICE);
batteryLevel = batteryManager.getIntProperty(BatteryManager.BATTERY_PROPERTY_CAPACITY);
} else {
Intent intent = new ContextWrapper(getApplicationContext()).
registerReceiver(null, new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED));
batteryLevel = (intent.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_LEVEL, -1) * 100) /
intent.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SCALE, -1);
}
return batteryLevel;
}
最后,完成前面添加的 onMethodCall() 方法,你需要处理单个平台方法 getBatteryLevel(),所以在参数 call 中对其进行验证。该平台方法的实现是调用上一步编写的 Android 代码,并使用 result 参数来返回成功和错误情况下的响应。如果调用了未知方法,则报告该方法。
移除以下代码:
new MethodChannel(flutterEngine.getDartExecutor().getBinaryMessenger(), CHANNEL)
.setMethodCallHandler(
(call, result) -> {
// This method is invoked on the main thread.
// TODO
}
);
并替换成以下内容:
new MethodChannel(flutterEngine.getDartExecutor().getBinaryMessenger(), CHANNEL)
.setMethodCallHandler(
(call, result) -> {
// This method is invoked on the main thread.
if (call.method.equals("getBatteryLevel")) {
int batteryLevel = getBatteryLevel();
if (batteryLevel != -1) {
result.success(batteryLevel);
} else {
result.error("UNAVAILABLE", "Battery level not available.", null);
}
} else {
result.notImplemented();
}
}
);
现在你应该可以在 Android 中运行该应用。如果使用了 Android 模拟器,请在扩展控件面板中设置电池电量,可从工具栏中的 ... 按钮访问。
步骤 4:添加 iOS 平台的实现
#首先在 Xcode 中打开 Flutter 应用的 iOS 宿主部分:
启动 Xcode
-
选择菜单项 File > Open...
-
导航到包含 Flutter 应用的目录,然后选择其中的 ios 文件夹。点击 OK。
在使用 Objective-C 的标准模板设置中添加对 Swift 的支持:
-
在项目导航中展开 Expand Runner > Runner。
-
打开项目导航
Runner > Runner下的AppDelegate.swift文件。
重写 application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: 方法并创建与 samples.flutter.dev/battery(channel 名)绑定的
FlutterMethodChannel:
@main
@objc class AppDelegate: FlutterAppDelegate {
override func application(
_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
let controller : FlutterViewController = window?.rootViewController as! FlutterViewController
let batteryChannel = FlutterMethodChannel(name: "samples.flutter.dev/battery",
binaryMessenger: controller.binaryMessenger)
batteryChannel.setMethodCallHandler({
[weak self] (call: FlutterMethodCall, result: FlutterResult) -> Void in
// This method is invoked on the UI thread.
// Handle battery messages.
})
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.register(with: self)
return super.application(application, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: launchOptions)
}
}
然后,添加 iOS Swift 代码,使用电池相关的 API 获取电量。这里的代码和你写原生 iOS 代码别无二致。
在 AppDelegate.swift 末尾添加以下新的方法:
private func receiveBatteryLevel(result: FlutterResult) {
let device = UIDevice.current
device.isBatteryMonitoringEnabled = true
if device.batteryState == UIDevice.BatteryState.unknown {
result(FlutterError(code: "UNAVAILABLE",
message: "Battery level not available.",
details: nil))
} else {
result(Int(device.batteryLevel * 100))
}
}
最后,完成前面添加的 setMethodCallHandler() 方法。你需要处理单个平台方法 getBatteryLevel(),所以在参数 call 中对其进行验证。该平台方法的实现是调用上一步编写的 iOS 代码。如果调用了未知方法,则报告该方法。
batteryChannel.setMethodCallHandler({
[weak self] (call: FlutterMethodCall, result: FlutterResult) -> Void in
// This method is invoked on the UI thread.
guard call.method == "getBatteryLevel" else {
result(FlutterMethodNotImplemented)
return
}
self?.receiveBatteryLevel(result: result)
})
首先在 Xcode 中打开 Flutter 应用的 iOS 宿主部分:
启动 Xcode
-
选择菜单项 File > Open...
-
导航到包含 Flutter 应用的目录,然后选择其中的 ios 文件夹。点击 OK。
确保 Xcode 项目构建没有错误。
-
打开项目导航 Runner > Runner 下的
AppDelegate.m文件。
创建一个 FlutterMethodChannel 并在
application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: 方法中添加 handler。确保使用与 Flutter 客户端相同的 channel 名称。
#import <Flutter/Flutter.h>
#import "GeneratedPluginRegistrant.h"
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication*)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary*)launchOptions {
FlutterViewController* controller = (FlutterViewController*)self.window.rootViewController;
FlutterMethodChannel* batteryChannel = [FlutterMethodChannel
methodChannelWithName:@"samples.flutter.dev/battery"
binaryMessenger:controller.binaryMessenger];
[batteryChannel setMethodCallHandler:^(FlutterMethodCall* call, FlutterResult result) {
// This method is invoked on the UI thread.
// TODO
}];
[GeneratedPluginRegistrant registerWithRegistry:self];
return [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions];
}
接下来添加使用 iOS battery API 来检索电池电量的 iOS Objective-C 代码。该代码与你在原生 iOS 应用中编写的代码完全相同。
在 AppDelegate 类中的 @end 之前添加以下方法:
- (int)getBatteryLevel {
UIDevice* device = UIDevice.currentDevice;
device.batteryMonitoringEnabled = YES;
if (device.batteryState == UIDeviceBatteryStateUnknown) {
return -1;
} else {
return (int)(device.batteryLevel * 100);
}
}
最后,完成前面添加的 setMethodCallHandler() 方法。你需要处理单个平台方法 getBatteryLevel(),所以在参数call 中对其进行验证。该平台方法的实现是调用上一步编写的 iOS 代码,并使用 result 参数来返回成功和错误情况下的响应。如果调用了未知方法,则报告该方法。
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
[batteryChannel setMethodCallHandler:^(FlutterMethodCall* call, FlutterResult result) {
// This method is invoked on the UI thread.
if ([@"getBatteryLevel" isEqualToString:call.method]) {
int batteryLevel = [weakSelf getBatteryLevel];
if (batteryLevel == -1) {
result([FlutterError errorWithCode:@"UNAVAILABLE"
message:@"Battery level not available."
details:nil]);
} else {
result(@(batteryLevel));
}
} else {
result(FlutterMethodNotImplemented);
}
}];
现在你应该可以在 iOS 中运行该应用。如果使用了 iOS 模拟器(注意它并不支持 battery API),应用则会显示 'battery info unavailable'。
步骤 5:添加 Windows 平台特定实现
#首先在 Visual Studio 中打开你 Flutter 应用 Windows 的 host 部分:
-
在你项目的目录夹下运行一次
flutter build windows以生成 Visual Studio solution 文件。 启动 Visual Studio。
-
选择 Open a project or solution
-
导航至含有你 Flutter 应用的目录下,然后进入 build 文件夹,然后是 windows 文件夹,然后选择
batterylevel.sln文件,点击 Open。
然后添加 platform channel 方法的 c++ 实现:
-
在 Solution 浏览器中展开 batterylevel > Source Files
打开
flutter_window.cpp。
首先,在文件的最顶部添加必要的引用,在 #include "flutter_window.h" 下面写上就行:
#include <flutter/event_channel.h>
#include <flutter/event_sink.h>
#include <flutter/event_stream_handler_functions.h>
#include <flutter/method_channel.h>
#include <flutter/standard_method_codec.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <memory>
编辑 FlutterWindow::OnCreate 方法,然后创建一个 flutter::MethodChannel
绑定 samples.flutter.dev/battery 名字:
bool FlutterWindow::OnCreate() {
// ...
RegisterPlugins(flutter_controller_->engine());
flutter::MethodChannel<> channel(
flutter_controller_->engine()->messenger(), "samples.flutter.dev/battery",
&flutter::StandardMethodCodec::GetInstance());
channel.SetMethodCallHandler(
[](const flutter::MethodCall<>& call,
std::unique_ptr<flutter::MethodResult<>> result) {
// TODO
});
SetChildContent(flutter_controller_->view()->GetNativeWindow());
return true;
}
接下来添加使用 Windows battery API 来检索电池电量的代码。该代码与你在原生 Windows 应用中编写代码别无二致。
在 flutter_window.cpp 顶部添加下面的新方法,在 #include 下面添加:
static int GetBatteryLevel() {
SYSTEM_POWER_STATUS status;
if (GetSystemPowerStatus(&status) == 0 || status.BatteryLifePercent == 255) {
return -1;
}
return status.BatteryLifePercent;
}
最后,完成 setMethodCallHandler() 方法。你可以在这里处理平台方法,getBatteryLevel(),然后可以在 call 参数中进行测试。这个平台方法调用的实现,在之前的步骤中已经完成了。如果调用了一个未知的,请报告它。
移除下面的代码:
channel.SetMethodCallHandler(
[](const flutter::MethodCall<>& call,
std::unique_ptr<flutter::MethodResult<>> result) {
// TODO
});
然后替换为这个:
channel.SetMethodCallHandler(
[](const flutter::MethodCall<>& call,
std::unique_ptr<flutter::MethodResult<>> result) {
if (call.method_name() == "getBatteryLevel") {
int battery_level = GetBatteryLevel();
if (battery_level != -1) {
result->Success(battery_level);
} else {
result->Error("UNAVAILABLE", "Battery level not available.");
}
} else {
result->NotImplemented();
}
});
You should now be able to run the application on Windows. If your device doesn't have a battery, it displays 'Battery level not available'.
Step 6: Add a macOS platform-specific implementation
#Start by opening the macOS host portion of your Flutter app in Xcode:
Start Xcode.
Select the menu item File > Open....
-
Navigate to the directory holding your Flutter app, and select the macos folder inside it. Click OK.
Add the Swift implementation of the platform channel method:
Expand Runner > Runner in the Project navigator.
-
Open the file
MainFlutterWindow.swiftlocated under Runner > Runner in the Project navigator.
First, add the necessary import to the top of the file, just after
import FlutterMacOS:
import IOKit.ps
Create a FlutterMethodChannel tied to the channel name
samples.flutter.dev/battery in the awakeFromNib method:
override func awakeFromNib() {
// ...
self.setFrame(windowFrame, display: true)
let batteryChannel = FlutterMethodChannel(
name: "samples.flutter.dev/battery",
binaryMessenger: flutterViewController.engine.binaryMessenger)
batteryChannel.setMethodCallHandler { (call, result) in
// This method is invoked on the UI thread.
// Handle battery messages.
}
RegisterGeneratedPlugins(registry: flutterViewController)
super.awakeFromNib()
}
}
Next, add the macOS Swift code that uses the IOKit battery APIs to retrieve the battery level. This code is exactly the same as you would write in a native macOS app.
Add the following as a new method at the bottom of MainFlutterWindow.swift:
private func getBatteryLevel() -> Int? {
let info = IOPSCopyPowerSourcesInfo().takeRetainedValue()
let sources: Array<CFTypeRef> = IOPSCopyPowerSourcesList(info).takeRetainedValue() as Array
if let source = sources.first {
let description =
IOPSGetPowerSourceDescription(info, source).takeUnretainedValue() as! [String: AnyObject]
if let level = description[kIOPSCurrentCapacityKey] as? Int {
return level
}
}
return nil
}
Finally, complete the setMethodCallHandler method added earlier.
You need to handle a single platform method, getBatteryLevel(),
so test for that in the call argument.
The implementation of this platform method calls
the macOS code written in the previous step. If an unknown method
is called, report that instead.
batteryChannel.setMethodCallHandler { (call, result) in
switch call.method {
case "getBatteryLevel":
guard let level = getBatteryLevel() else {
result(
FlutterError(
code: "UNAVAILABLE",
message: "Battery level not available",
details: nil))
return
}
result(level)
default:
result(FlutterMethodNotImplemented)
}
}
You should now be able to run the application on macOS. If your device doesn't have a battery, it displays 'Battery level not available'.
Step 7: Add a Linux platform-specific implementation
#
For this example you need to install the upower developer headers.
This is likely available from your distribution, for example with:
sudo apt install libupower-glib-dev
Start by opening the Linux host portion of your Flutter app in the editor of your choice. The instructions below are for Visual Studio Code with the "C/C++" and "CMake" extensions installed, but can be adjusted for other IDEs.
Launch Visual Studio Code.
Open the linux directory inside your project.
-
Choose Yes in the prompt asking:
Would you like to configure project "linux"?. This enables C++ autocomplete. Open the file
runner/my_application.cc.
First, add the necessary includes to the top of the file, just
after #include <flutter_linux/flutter_linux.h>:
#include <math.h>
#include <upower.h>
Add an FlMethodChannel to the _MyApplication struct:
struct _MyApplication {
GtkApplication parent_instance;
char** dart_entrypoint_arguments;
FlMethodChannel* battery_channel;
};
Make sure to clean it up in my_application_dispose:
static void my_application_dispose(GObject* object) {
MyApplication* self = MY_APPLICATION(object);
g_clear_pointer(&self->dart_entrypoint_arguments, g_strfreev);
g_clear_object(&self->battery_channel);
G_OBJECT_CLASS(my_application_parent_class)->dispose(object);
}
Edit the my_application_activate method and initialize
battery_channel using the channel name
samples.flutter.dev/battery, just after the call to
fl_register_plugins:
static void my_application_activate(GApplication* application) {
// ...
fl_register_plugins(FL_PLUGIN_REGISTRY(self->view));
g_autoptr(FlStandardMethodCodec) codec = fl_standard_method_codec_new();
self->battery_channel = fl_method_channel_new(
fl_engine_get_binary_messenger(fl_view_get_engine(view)),
"samples.flutter.dev/battery", FL_METHOD_CODEC(codec));
fl_method_channel_set_method_call_handler(
self->battery_channel, battery_method_call_handler, self, nullptr);
gtk_widget_grab_focus(GTK_WIDGET(self->view));
}
Next, add the C code that uses the Linux battery APIs to retrieve the battery level. This code is exactly the same as you would write in a native Linux application.
Add the following as a new function at the top of
my_application.cc just after the G_DEFINE_TYPE line:
static FlMethodResponse* get_battery_level() {
// Find the first available battery and report that.
g_autoptr(UpClient) up_client = up_client_new();
g_autoptr(GPtrArray) devices = up_client_get_devices2(up_client);
if (devices->len == 0) {
return FL_METHOD_RESPONSE(fl_method_error_response_new(
"UNAVAILABLE", "Device does not have a battery.", nullptr));
}
UpDevice* device = UP_DEVICE(g_ptr_array_index(devices, 0));
double percentage = 0;
g_object_get(device, "percentage", &percentage, nullptr);
g_autoptr(FlValue) result =
fl_value_new_int(static_cast<int64_t>(round(percentage)));
return FL_METHOD_RESPONSE(fl_method_success_response_new(result));
}
Finally, add the battery_method_call_handler function referenced
in the earlier call to fl_method_channel_set_method_call_handler.
You need to handle a single platform method, getBatteryLevel,
so test for that in the method_call argument.
The implementation of this function calls
the Linux code written in the previous step. If an unknown method
is called, report that instead.
Add the following code after the get_battery_level function:
static void battery_method_call_handler(FlMethodChannel* channel,
FlMethodCall* method_call,
gpointer user_data) {
g_autoptr(FlMethodResponse) response = nullptr;
if (strcmp(fl_method_call_get_name(method_call), "getBatteryLevel") == 0) {
response = get_battery_level();
} else {
response = FL_METHOD_RESPONSE(fl_method_not_implemented_response_new());
}
g_autoptr(GError) error = nullptr;
if (!fl_method_call_respond(method_call, response, &error)) {
g_warning("Failed to send response: %s", error->message);
}
}
你现在应该可以在 Linux 上运行应用了。如果你的设备没有电池的话,它会提示 'Battery level not available'。
使用 Pigeon package 调用特定平台的代码
#
你可以使用 Pigeon package 替代 Flutter 的平台通道 API,它将生成以结构化、类型安全方式发送消息的代码。
Pigeon 的工作流程如下:
-
Flutter 应用程序通过平台通道向其 主机(应用程序的非 Dart 部分)发送结构化的类型安全信息。
-
主机通过平台通道监听并接收消息。然后,它使用原生编程语言调用任意数量的特定平台 API,并将响应发送回 客户端(应用程序的 Flutter 部分)。
使用该 package 消除了在主机和客户端之间匹配字符串需要的消息名称和数据类型。它支持嵌套类、消息转换为 API、生成异步封装代码,以及任一方向发送消息。生成的代码具有相当的可读性并保证在不同版本的多个客户端之间没有冲突。
有了 Pigeon,消息传输协议就可以在 Dart 的子集中定义,然后为 Android、iOS、macOS 以及 Windows 生成消息传输代码。例如:
import 'package:pigeon/pigeon.dart';
class SearchRequest {
final String query;
SearchRequest({required this.query});
}
class SearchReply {
final String result;
SearchReply({required this.result});
}
@HostApi()
abstract class Api {
@async
SearchReply search(SearchRequest request);
}
import 'generated_pigeon.dart';
Future<void> onClick() async {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest(query: 'test');
Api api = SomeApi();
SearchReply reply = await api.search(request);
print('reply: ${reply.result}');
}
你可以在 pub.dev 上的 pigeon 页面找到完整的示例和更多信息。
通道和平台线程
#
目标平台向 Flutter 发起 channel 调用的时候,需要在对应平台的主线程执行。同样的,在 Flutter 向目标平台发起 channel 调用的时候,需要在根 Isolate 中执行。对应平台侧的 handler 既可以在平台的主线程执行,也可以通过事件循环在后台执行。对应平台侧 handler 的返回值可以在任意线程异步执行。
Use plugins and channels from a background isolate
#
Plugins and channels can be used by any Isolate, but that Isolate has to be
a root Isolate (the one created by Flutter) or registered as a background
Isolate for a root Isolate.
The following example shows how to register a background Isolate in order to
use a plugin from a background Isolate.
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:shared_preferences/shared_preferences.dart';
void _isolateMain(RootIsolateToken rootIsolateToken) async {
BackgroundIsolateBinaryMessenger.ensureInitialized(rootIsolateToken);
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = await SharedPreferences.getInstance();
print(sharedPreferences.getBool('isDebug'));
}
void main() {
RootIsolateToken rootIsolateToken = RootIsolateToken.instance!;
Isolate.spawn(_isolateMain, rootIsolateToken);
}
在后台线程中执行通道 handler (Android)
#要在 Android 应用程序的后台线程上执行通道的 handler,需要使用 Task Queue API。
override fun onAttachedToEngine(@NonNull flutterPluginBinding: FlutterPlugin.FlutterPluginBinding) {
val taskQueue =
flutterPluginBinding.binaryMessenger.makeBackgroundTaskQueue()
channel = MethodChannel(flutterPluginBinding.binaryMessenger,
"com.example.foo",
StandardMethodCodec.INSTANCE,
taskQueue)
channel.setMethodCallHandler(this)
}
@Override
public void onAttachedToEngine(@NonNull FlutterPluginBinding binding) {
BinaryMessenger messenger = binding.getBinaryMessenger();
BinaryMessenger.TaskQueue taskQueue =
messenger.makeBackgroundTaskQueue();
channel =
new MethodChannel(
messenger,
"com.example.foo",
StandardMethodCodec.INSTANCE,
taskQueue);
channel.setMethodCallHandler(this);
}
在后台线程中执行通道 handler(iOS)
#要在 iOS 应用程序的后台线程上执行通道的 handler,需要使用 Task Queue API。
public static func register(with registrar: FlutterPluginRegistrar) {
let taskQueue = registrar.messenger().makeBackgroundTaskQueue?()
let channel = FlutterMethodChannel(name: "com.example.foo",
binaryMessenger: registrar.messenger(),
codec: FlutterStandardMethodCodec.sharedInstance(),
taskQueue: taskQueue)
let instance = MyPlugin()
registrar.addMethodCallDelegate(instance, channel: channel)
}
+ (void)registerWithRegistrar:(NSObject<FlutterPluginRegistrar>*)registrar {
NSObject<FlutterTaskQueue>* taskQueue =
[[registrar messenger] makeBackgroundTaskQueue];
FlutterMethodChannel* channel =
[FlutterMethodChannel methodChannelWithName:@"com.example.foo"
binaryMessenger:[registrar messenger]
codec:[FlutterStandardMethodCodec sharedInstance]
taskQueue:taskQueue];
MyPlugin* instance = [[MyPlugin alloc] init];
[registrar addMethodCallDelegate:instance channel:channel];
}
跳转到 UI 线程 (Android)
#
为了符合通道跳转到 Android UI 线程的要求,你可能需要从后台线程跳转到 Android 的 UI 线程以执行通道的方法。在 Android 中的实现方式是:在一个叫 Looper 的 Android UI 线程里 post() 一个 Runnable。这能使得 Runnable 的下一个时机在主线程上执行。
Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post {
// Call the desired channel message here.
}
new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Call the desired channel message here.
}
});
跳转到主线程 (iOS)
#为了符合通道跳转到 iOS 主线程的要求,你可能需要从后台线程跳转到 iOS 的主线程来执行通道方法。在iOS中,这是通过在主 dispatch queue 上执行 block 来实现:
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
// Call the desired channel message here.
});
DispatchQueue.main.async {
// Call the desired channel message here.
}
Supplementals
#Common channels and codecs
#The following is a list of some common platform channel APIs that you can use to write platform-specific code:
-
MethodChannelfor Flutter: A named channel that you can use to communicate with platform plugins using asynchronous method calls. By default this channel uses theStandardMessageCodeccodec. This channel is not type safe, which means calling and receiving messages depends on the host and client declaring the same arguments and data types in order for messages to work. -
BasicMessageChannelfor Flutter: A named channel that supports basic, asynchronous message passing, using a supported message codec. Not type safe. -
Engine Embedder APIs for Platforms: These platform-specific APIs contain platform-specific channel APIs.
You can create your own codec or use an existing one. The following is a list of some existing codecs that you can use with platform-specific code:
-
StandardMessageCodec: A commonly used message codec that encodes and decodes a wide range of data types into a platform-agnostic binary format for transmission across platform channels. The serialization and deserialization of values to and from messages happens automatically when you send and receive values. For a list of supported data types, see Platform channel data types support. -
BinaryCodec: A message codec that passes raw binary data between the Dart side of your Flutter app and the native platform side. It does not perform any higher-level encoding or decoding of data structures. -
StringCodec: A message codec that encodes and decodes strings, using UTF-8 encoding. -
JSONMessageCodec: A message codec that encodes and decodes JSON-formatted data, using UTF-8 encoding. -
FirestoreMessageCodec: A message codec that handles the exchange of messages sent across the platform channel between your Flutter app and the native Firebase Firestore SDKs (on Android and iOS).
Separate platform-specific code from UI code
#If you expect to use your platform-specific code in multiple Flutter apps, you might consider separating the code into a platform plugin located in a directory outside your main application. See developing packages for details.
Publish platform-specific code as a package
#To share your platform-specific code with other developers in the Flutter ecosystem, see publishing packages.
除非另有说明,本文档之所提及适用于 Flutter 3.38.6 版本。本页面最后更新时间:2025-10-28。查看文档源码 或者 为本页面内容提出建议。